Water resources in Jordan are extremely limited. The largest water consume is prior taken from Agriculture, taking about 70 % of the national water budget. The use of treated waste water for irrigation is a national objective with the aim to substitute freshwater by treated waste water. The current practice of use of the treated effluent is inadequate in terms of environment and health and inefficient in terms of irrigation.
Future effluent volumes are expected to increase substantially, hence could replace - when used properly - large amounts of fresh water to the benefit of drinking water supply. The envisaged agricultural area to be irrigated with treated wastewater (mixed with fresh water) is more than 5000 ha. It is expected that the utilization of treated waste water will increase between 2015 and 2035 from 7.5 Million m³ to 15 Million m³.
An additional and promising side benefit is the reuse of treated wastewater for hydropower production making use of the unique topography of up to 600 m of head from the Jordan highlands down to the Jordan valley. Depending on the alternative selected, hydropower turbines of a capacity of up to 4 MW can be installed.
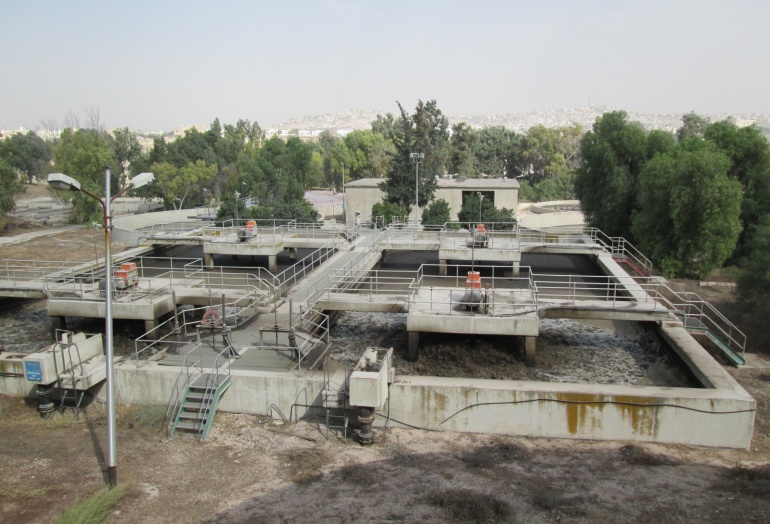
The irrigation area is located in the Northern Jordan Valley. The Greater Irbid Area is the catchment of effluent of the Waste Water Treatment Plants (WWTP) of Wadi Arab, Central Irbid and Wadi Shallala with following characteristics:
No |
Name |
Design Capacity 2025in PE - Daily Wastewater Flow |
Design Capacity 2035in PE - Daily Wastewater Flow |
|
1 |
WWTP Wadi Arab |
251,000 - 22,350 m³/d | 315,000 - 28,000 m³/d |
|
2 |
WWTP Central Irbid |
140,000 - 13,350 m³/d | 169,000 - 16,150 m³/d |
|
3 |
WWTP Wadi Shallala |
166,000 - 16,400 m³/d |
-- |
The existing FS (also done by GITEC/AHT/CEC) differentiates 2 alternatives of technical facilities for reuse. Alternative 1 features the reuse of Treated Waste Water (TWW) during irrigation seasons only, whilst Alternative 2 aims at utilization of all TWW by the construction of a dam and wastewater retention reservoir. The TOR favours a combination of both alternatives. Since the existing FS considers all alternatives as “stand alone”, a crucial task for the update of the FS is to combine those alternatives. The new alternative shall initially permit the direct injection of TWW into the existing irrigation system with the possibility to extend it by an intermediate storage reservoir for TWW at Wadi Darraba at a later stage. Immediately after the decision on reuse components included, surveys and investigations regarding site selection and alignment of pipes will be carried out.
The project includes the entire tendering process for supply of material and equipment and construction services. Subsequently, the Consultant will provide site supervision to ensure highest quality of construction as well as to control and monitor quantity, cost and completion schedules agreed upon in the contract.
Services Provided
The Project comprises four Phases:
Phase I+II: Updating of existing FS / Preparation of Final Design and Tendering
- Reviewing / Updating of relevant parts of the existing FS from 2005 (e. g. waste water quantities and qualities, economic and financial feasibility etc.) including the acceptance of the reuse of treated wastewater for agriculture purposes and the identification of the crops which could be irrigated.
- Final Design and Tender Documents including transmission and distribution pipelines and the extension of 2 activated sludge treatment plants. The tender documents were prepared on the basis of FIDIC yellow (waste water treatment facilities) and red book (pipelines, mixing stations, pumping stations etc.) conditions of contract.
- Tendering and Contracting
Phase III: Site Supervision of Works
- Assistance to the Client in supervision and physical progress and quality of works
- Monitoring of construction costs
- Provisional acceptance/taking over
Phase IV: Assistance to the Client during DLP
- Review and Approval of O&M processes and manuals
- Final testing and inspection of facilities
- Final Acceptance